Overview
The overview page summarizes the most important metrics regarding the security posture of the firmware image. Let’s review the information presented in this aggregated report!
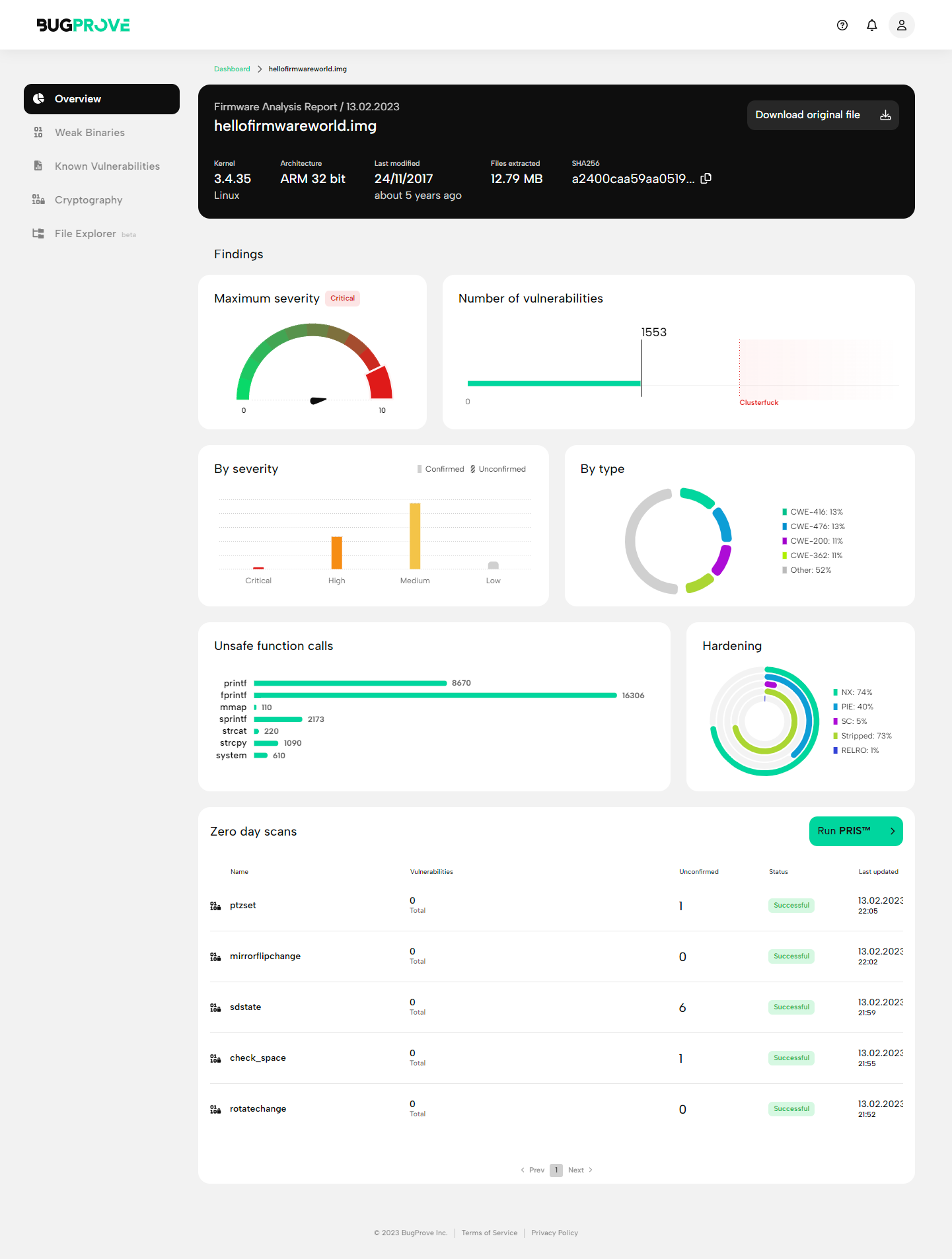
Header
- Top row
- Name (e.g. hellofirmwareworld.img) and scan date
- SHA-256 digest (e.g. e34eb7ae410994ab…)
- Bottom row
- Kernel (e.g. Linux 5.4.217, FreeBSD 12.2)
- Architecture (e.g. ARM, MIPS-BE, x86-64)
- Files extracted (e.g. 15.4 MB, 1220)
- Last modified (e.g. 2020-04-04, 2 years ago)
You can also use the “Download original file” button to download a copy of the file you have uploaded.
Findings
- Maximum severity: the highest CVSS score amongst the vulnerabilities found.
- Number of vulnerabilities: logarithmic chart of the total number of findings.
- By severity: distribution of findings by severity, calculated from their CVSS score.
- By type: distribution of findings by type, as determined by their CWE number.
Binaries
Unsafe function calls
When we discover binaries in a firmware image, we perform a quick static analysis to determine whether the binary calls any of the known unsafe functions listed here. This can be helpful when trying to determine the overall coding style of the vendor and to get a bird’s eye view of potential risks. This graph is a summary of all binaries present on the system - for a per binary view, see Weak binaries.
Hardening
We also check binaries for commonly used hardening techniques. The more of these techniques are present, and the greater the number of executables they cover, the better. Each ring on the graph represents a hardening measure, with a full ring indicating that it is present on all binaries.
Zero-day scans
Lists PRIS™ zero-day scans started for individual binaries found in the firmware image. By default, such scans are automatically started for the 5 most likely to be vulnerable binaries, but this can be disabled when starting scans. Additional zero-day scans can be started on the Weak binaries page via the Run PRIS™ button. Findings by PRIS™ start as Unconfirmed - they need to be accepted before they count as findings (or rejected, in case of false positives).